Cost Benefit Analysis of Smart Grids
This project focuses on fundamental, cross-cutting issues that will provide a better understanding of Smart Grid ecosystems among stakeholders. It seeks to establish interfaces with existing networks/initiatives, establishing synergies and avoiding duplication of ongoing activities.
The International Smart Grid Action Network (ISGAN) promotes (based also on Swiss participation) a mechanism for multilateral government-to-government collaboration to advance the development and deployment of smarter electric grid technologies, practices, and systems. It aims to improve the understanding of Smartgrid technologies, practices, and systems and to promote adoption of related enabling government policies.
A number of ISGAN projects have been established for various Smartgrid technology domains. The initial Annexes focus on fundamental, cross-cutting issues that will provide a better understanding of Smartgrid ecosystems among the Participants. The Annexes seek to establish interfaces with existing networks/initiatives, establishing synergies and avoiding duplication of ongoing activities.
Results
The Tasks and Subtasks within the ISGAN Annex III are carried out on a task-sharing basis, as directed by the ISGAN ExCo. The following summary of activities includes contributions of all participating countries to the tasks. More insights have been reached on the smartness methods proposed as a benchmark
- the Smart Grids Maturity Model - SGMM - developed by Software Engineering Institute at Carnegie Mellon University
- the Katholieke Universiteit Leuven (KUL) smart grid maturity model
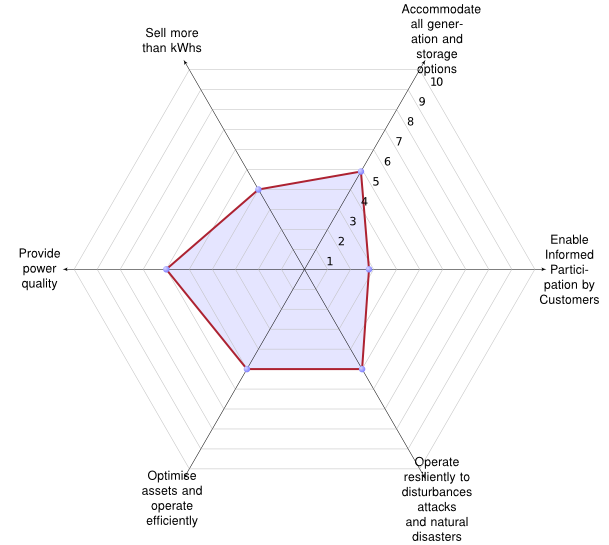
Main quantitative innovation of Belmans’ method (KUL) is the clear definition of a wide set of KPIs, proposed for assessing the “smartness” of an electricity grid. In a Smart Grid context,a common view may be lost: each stakeholder proposes his point of view, aimed at his specific
targets. Revisions to the KUL approach have been made to take into consideration also market features of the smart grids. Furthermore a web-based questionnaire has been developed for the initial smartness assessment of some on-going smart grid projects in participating countries.
The ESC member involved in this project is Dr. Turhan Demiray at the Research Centre for Energy Networks of ETH Zurich (Forschungsstelle Energienetze - FEN) at ETH.
The FEN was established in June 2011 to contribute to answering the energy challenges of today and the future towards a more sustainable energy system with a special focus on energy networks by means of independent, credible, applied and interdisciplinary research.